types of rainfall
Different types of rainfall occurs water moves from the streams or rivers up to there, forming clouds and the sky. Also, water goes from sea to sky. All these are part of the hydrologic cycle or water cycle. This cycle makes water move from sky to river and sea to sky. Without it, we cannot have lakes, streams, and even the sea. Therefore without this cycle, it will not be possible for animals or humans to live at all. Following are some stages of the water cycle:
- The cycle starts at sea, where water is warmed by the sun. Rainfall causes the evaporation of seawater. Thus seawater turns to water, steam and then vapour. This till vapour rises as when hot air tends to be light.
- With the very height, water evaporation becomes cooler. This cooling causes the water vapour to condense as the cooler cannot store water droplets.
- When the vapour less, formed are clouds. This cloud adds more and more vapour until it cannot store any more after saturation of the cloud rain starts.
- According to temperature, types of precipitation has many forms. Thus it can include sleet, or snow rain, hailstones.
- This rain flows into streams and rivers, and these streams and rivers bring the water back to the sea, where the water cycle starts again.
Types of rainfall
The following five types of rainfall
Convective rain
When the heats, a shallow layer of air closes, and the Sun shines on the ground. This air is warmer than the surrounding air, so it goes up in the atmosphere (warm air rises). The higher you rise in the atmosphere, the colder it is. So the warm air that has risen in the atmosphere now starts to cool down the air. As a result, the water vapour condenses into water, forms a cloud, and eventually falls as rainfall.
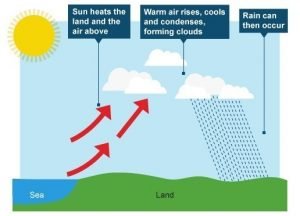
This type of rain is also known as usually produces smaller areas of rain and showers, which is why on some days you may get rain down, although a neighbouring village may have stayed dry. This is the type of situation where you will have rain on the day, with sunshine in between and rainfall that seems like the weather cannot make its mind up.
Showers are very small in size and are much more unpredictable because the ground surface varies greatly across each country. This means the air close to the ground is heated at different layers, which is why the showers can go anywhere and be blown around in different directions of the air. If, for example, available tarmac on the ground (a depth surface), this will heat the air more quickly than one made of water (such as a lake) or a lighter surface (such as grass).
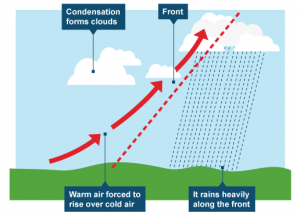
Frontal rainfall:
The meeting of a large mass of warm air and a large mass of cold air is called a front. The meeting creates turbulence. A frontal rain diagram can illustrate how the warm air goes up over the cold air and forms large clouds when its moisture and cools condenses. Thunderstorms, complete with lightning, are the usual result, and they can last anywhere from some minutes to more or an hour.
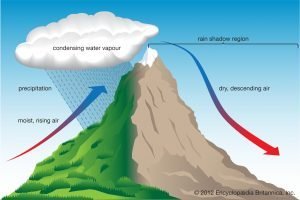
Relief Rainfall
This type of rainfall is common in places with seas and mountains. More rainfall frequently occurs near mountains beside the sea areas. The moisture-laden wind blows in from the sea because the wind mixes a high mountain, and hence the air is forced to rise upwards. At the height of vapour, the air is cooled, and then the cloud is formed.
This saturated cloud with water vapour starts to precipitate on the side of the mountain facing the sea area. This front side of the mountain is called the direction side.
The cloud mostly rains on the windward (air direction) side of the mountain. Although, the cloud meets another side, which is called the leeward (lift direction) side. Since the cloud has already lost most of the cloud moisture, so it rains very little there.
This makes leeward sides of a mountain area rain little rain. As a result, there is a much moist climate on the windward sides of slopes. On the other hand, there is a very dry, sheltered climate available on the leeward side. This rainfall is common in the Sierra Nevada, the Andes, and Hawaii.
Monsoonal rainfall:
The Earth’s rotation creates and combines the sun’s heat band of easterly winds at 30 degrees south and north latitude. This vapour air blows all year, but wind changes direction with the seasons. This seasonal shift is responsible for monsoon rains in Southeast Asia, India, and other places.
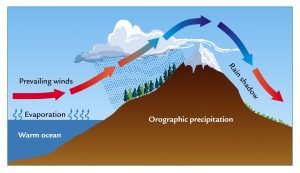
Orographic rainfall:
When moisture-laden air encounters a mountain range, the air is forced to grow up. As a result, orographic rainfall cools off at the higher elevation, condensing water out of the created rainfall and air. If the temperature is very cold, the rain falls as snow.