Scaffolding parts and types
Different scaffolding parts and types are used while constructing the temporary works for holding concrete work etc.
The term scaffolding is generally used for the temporary structure used to support the concrete structure scaffolding or, more popularly, for supporting the worker during the construction (plastering, and brickwork or painting or repainting or renewal of structures, etc.).
Scaffolding comes under safety regulations on construction sites. Therefore, use and standards have been prescribed for its layout.
For example, when a man is liable to fall from more than 3 meters height, he should be provided with a 2meter height of guardrail and a toe board at least 0.2 meters above the platform.
All the accidents, about 30 to 44 per cent of that occur in building construction sites, are due to consequent falls of persons from heights and faulty scaffolding. Therefore, strong supervision should be taken in putting up formwork according to standard practices.
To minimize accidents on the construction site due to faulty scaffolding or formwork, we can try the hiring industry experienced people like Bristol scaffolding.
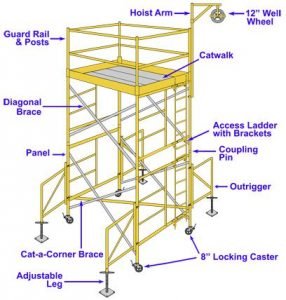
Parts of Scaffolding.
Scaffolding gave the following parts.
- Standards: also called uprights The vertical posts.
- Ledgers: The horizontal members parallel to the wall of the building.
- Braces: The bracing system is mostly made of wood planks.
- Putlogs: Horizontal members normal to the wall of the building.
- Transoms: Putlogs whose both ends are supported on ledgers in double formwork.
- Bridle: this Member used to bridge openings.
- Boarding: it is Planks on which workers stand.
- Guard rail: the Rail provided at about 1 m level to guard the men working on the boarding or (planks).
- Toeboard: Boards placed parallel to boarding near the wall to give protection to workmen
- Soleplate or Baseplate: Plates on the ground supporting standards.
- Base jack: Sometimes known as the soleplate, the base jack is the load-bearing base for the formwork that certain plates are placed on the ground. The base jack supports the vertical poles, called standards, that form the scaffold.
- Scaffold tie: Scaffold ties are used to secure the formwork to other structures.
- Some scaffolds come with different stairways or ladder types to help workers overcome and climb on and off physical obstacles. Others may also have rubbish chutes to remove unwanted materials from the formwork safely.
Types of Scaffolding.
Some of the common types of scaffolding:
Single scaffolding for bricklayers scaffolding.
Single scaffolding is mostly used for brickwork and consists of an outer row of verticals to which longitudinal members are tied at different levels of work.
Rest on the walls being built inside, and putlogs are tied to the standards at the outer end. The platform is carried on the cross member (putlogs).

If the (putlog) cross-level coincides with an opening in the wall, the putlog cannot be placed on the wall. Hence, the putlog should rest on a cross piece (called bridle tube) tied at the wall end of the adjacent putlogs.
Cross bracing(wood planks) in the vertical planes between the verticals is also introduced for lateral stability.
Where the vertical posts cannot be in holes made in the ground or placed on base plates, vertical posts should be suitably placed and braced for lateral stability.
A popular method in such cases is to place the vertical post of suitable diameter filled with compacted earth and in a steel barrel of 0.6 meters in height.
Double scaffolding or Mason’s scaffolding.
This is a supporting system used for plastering. Double scaffolding has pairs of (outer or inner) verticals. Instead of being supported on the wall, the putlogs are supported on an interior system of longitudinal and verticals.

To give additional lateral stability to the tall and narrow framework, double scaffolding is tied to the building at intervals when used for rising buildings.
Cantilever or needle scaffolding.
To construct the upper part of a rise residential building, they eliminate unwanted scaffolding at lower levels keeping the space free for transport, etc.

The needle scaffolding is similar to the double scaffold, except that needle scaffolding is supported at the bottom by a cantilever prop.
Birdcage scaffolding.
Birdcage scaffolding is used for internal work and consists of a simple cage supported on four verticals from which the workmen can work.

Birdcage scaffolding is movable and can be easily moved from one place to another place.
Ladder or trestle scaffolding.
This is usually portable and is used for light work. Ladder scaffolding consists of two ladders with the top joined ends together by planks to work on this platform.

Suspended scaffolding.
In rise buildings for working at high levels, such as the painting of rising buildings, suspending scaffolding is economical and more convenient to suspend the working platform from above the ground than to support it from the ground.

Suspend scaffolding is especially so when the height is more than 30 to 35 meters.
They are of three types operated by winches and fixed and operated by pulleys.
