What is Beam? IT’S TYPES, SIZES, PURPOSE

A beam is a horizontal structural member in a building to resist the lateral loads applied to the beam’s axis. The structural member which resists the forces laterally or transversely applied to the (beam) axis is called a beam.
The loads act transversely to the longitudinal axis, which produces the shear forces and bending moment. The lateral load acting on beams is the main cause of the bending of the beam. They are responsible for transferring a load from the slab to the column. The load distribution pattern is,
Slab |> Beam |> Column |> Foundation
That beam is connected with the column, and this connection is called direct support, while the beam connects with the beam, which is called indirect support.
Purpose of beams
It is a structural element that is capable of withstanding load primarily by resisting its bending forces. They are made of steel or reinforced concrete (RCC)or steel. We use it in structure to
- Resist loads
- Counter bending moment and shear forces.
- Connect the frame.
- Provide a uniform distribution of loads.
In the beam, the different reinforcements were used having other purposes such as
- Support bars – These bars are located in the top portion of the beam and just function to hold the stirrups in place.
- Main Bars – Provide to carry loads (Moments).
- Stirrups – To counter the shear stresses (shear force).
They are generally characterized by their profile (shape, cross-section, length, material). This member of RCC structures is placed horizontally to carry the load and counter both bending and shear stresses.
The standard size of the beams,
- A residential building is 9 ʺ × 12 ʺ or 225 mm × 300 mm according to the (IS codes).
- The minimum size of the RCC beam should not be less than 9 ʺ× 9 ʺ or 225mm × 225mm with the addition of slab thickness which is 125mm.
Purpose of stirrups in the beam.
- Stirrups are used to counter the shear force. It is also called shear reinforcement in the beam.
- Shear force is maximum at the end supports (simply supported beams) and zero at the mid-span. That’s why the spacing of stirrups or rings is close to each end support compared to the middle.
- Stirrups are made in a rectangular shape with reinforcement bars wrapped around the beam’s top and bottom bars.
- Sometimes, stirrups are placed diagonally and vertically to avoid shear failure in case of cracks in beams.
Classification of beams:
Generally, beams are classified by the shape of their cross-section, their length, and by their equilibrium conditions.
According to the support conditions:
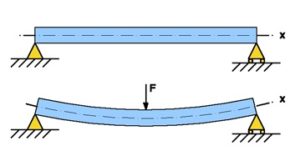
1: Simply supported beams:
A simply supported beam is supported at both ends. These beams are primarily used in general construction.
- Supported freely to rotate at the two ends on walls or columns.
- Have no moment of resistance at support.
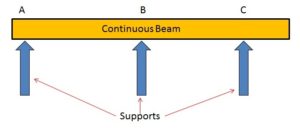
2: Continuous beams:
A beam that has more than two supports this kind of beam is called a continuous beam. Two or more two supports are used between these beams, and these beams are similar to the simply supported beams.
- Supported on two or more vertical supports.
- It is considered a more economical beam as compared to others.
- The beam over which both sides have an overhanging is called a double overhanging beam.
3: Fixed beams:
A beam that is fixed at both ends is called a fixed beam. Fixed beams are not allowed the vertical movement or rotation of the beam. In this beam, no bending moment will produce. Fixed beams are only under the shear force and are generally used in trusses and other structures.
- Both ends of the beam are rigidly fixed with supports.

4: cantilever beams:
A fixed beam at one end and accessible on the other end is called an overhanging beam. These beams carry loads of both shear stress and bending moment. These beams are generally used in bridge trusses and other structural members.
- It’s one end fixed in-wall or column, and the other side is free.
- In the cantilever, the tension zone is located at the top and compression at the bottom.

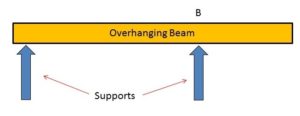
5: Overhanging beam:
A beam supported by two points but on the third point hanging or not helping is called an overhanging beam. It is a combination of the cantilever and the simply supported beam.
- Its ends extend beyond the columns or walls.
- The overhanging portion is unsupported or may locate on both sides of the beam.
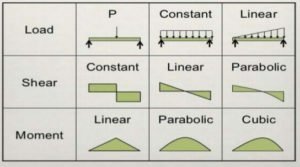
Types of loads on beams
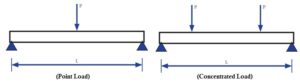
1: Point load or concentrated load
The point load is defined as a load applied to a single location of the whole span length.
- It is also called a concentrated load.
- Act over a small distance.
- The load is denoted by P, and the arrow shows the load direction.
2: Distributed Load:
This load is divided into two main loads such as,
Uniformly distributed load (UDL)
The loading magnitude remains the same for the whole span, called uniformly distributed load.
- It is denoted by q or w.
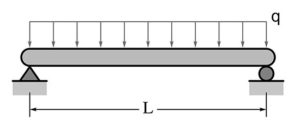
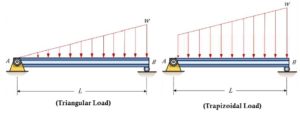
Uniformly varying load (UVL)
The load whose magnitude is continuously varying throughout the span.
- It is also called a non-uniformly distributed load.
- It is also divided into two different types Triangular or Trapezoidal Load.
3: Couple Forces
This force act on the same span having the same load and opposite forces.
- In the case of unequal load, one force makes them rotate.
- Expresses as kip.m, kg.m, N.m, lb.ft etc.
Reinforcement in RCC Beam
1: Single reinforcement
The reinforcement is provided in the tension zone called a single reinforcement beam.
- Responsible for carrying ultimate bending moment and tension.
- Compression is countered by concrete.
- Practically this is not applicable.
2: Double reinforcement
The reinforcement is provided in both zones (Tension and compression).
- Double reinforcement is used when the depth is restricted.
- This reinforcement beam is used in structures.
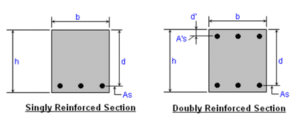
Clear the concepts of the following terms,
Shear force:
- The algebraic sum of all forces acting on either side of the section is known as shear force.
Bending moment:
- Any moment is produced in a beam due to applying load on them. The element causes to bend under this phenomenon is known as the bending moment.
Deflection:
- Deflection in a beam is produced by loads, temperature, poor construction and settlement, and bending moment and axial force.
Also Read:
If you like this information, Share it with your friends…
We Love CricketAdd a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.

nice information.Thank you for sharing.
Thanks very much for sharing I enjoyed it