TYPES OF COLUMNS ACCORDING TO LOADS AND ITS LENGTHS
Different Types of columns are used in the vertical structural member that can carry compressive forces. It is responsible for transferring the loads from slabs to the beam to the foundation. Therefore, the column is an essential structural member of the building; without the queue, you cannot construct an RCC building or structure (Strong).
Additional loads from the snow, wind and other horizontal forces can cause the column to bend. Columns can also carry primary axial loads and are designed for compression.
Before going into the detail of columns types, lets clear the following concepts first,
Buckling:
- Buckling is also known as a failure in the column due to compressive action on the structural member or element.
- The sudden significant failure or deformation of the structure due to a slight increase of an existing load under which the design has exhibited little.
According to the RCC column, the columns are classified into different types, according to load, and based on lengths, so let’s jump into the detail.
Types of columns:
We differentiated the RCC column according to the,
- Members reinforced with the longitudinal bars and lateral ties.
- Member reinforced with the longitudinal bars and the continuous spirals.
- Composite compression member reinforced with structural steel shapes, pipe, and with or without longitudinal bars and lateral reinforcements.
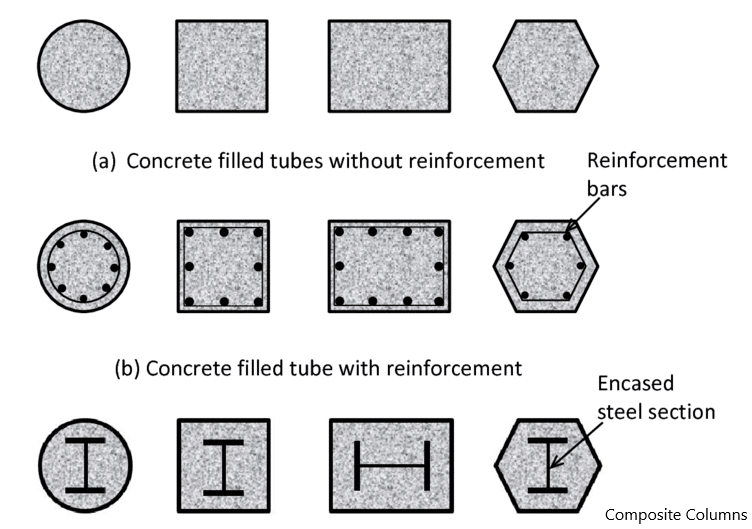
The main types are,
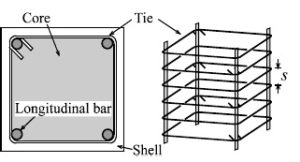
1: Tied columns
- The column in which the lateral ties are closely spaced throughout the column.
- The spacing of ties is limited and close enough to prevent barrelling failures and far enough not to interface the setting of concrete.
- According to ACI 7.10.5: The ties’ vertical spacing must be between 16D of the longitudinal bar (D is the diameter of the bar) and 48D from the diameter of the link.
- If the spacing of the ties is too far, the column then may face a shear failure.
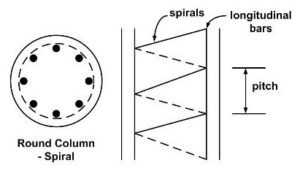
2: Spiral columns
- Are those columns in which the winding bar is wrapping around the column longitudinal reinforcements.
- The spirals around the column provide support and prevent the column from barreling.
- ACI Code 7.10.4.2: The size of spirals shall not be less than 3/8 in diameter.
- ACI Code 7.10.4.3: The spacing or pitch of spirals shall not exceed 3 in, nor be less than 1 in.
- These columns are mainly constructed in round shapes.
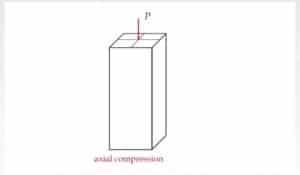
Types of columns based on load condition:
1: Axially loaded column
- The load is subjected to the center of the column.
- The load act on the longitudinal axis.
- According to IS: 456-2000, The longitudinal reinforcement cross-sectional area is not less than 0.8% or not more than 0.6% of the column’s cross-sectional area.
- The minimum longitudinal bar not less than 4 No’s in rectangular and not less than 6 No’s in the circular column.
- The minimum diameter of the bar is not less than 12mm.
2: Eccentric column
- In this, the load is acting on the column to the offset from the centroid of the column.
- The offsets loading on the column is referred to as eccentric loading.
- The moment on the column was increased due to the eccentric load increases the axial load and the moment acting on the column.
- With this, the bending of the column was also increased.
Types of columns according to a length:
1: Short columns:
- A column is short when its length is such that the lateral buckling need not be considered.
- When the ratio of the effective length to the minor lateral dimensions of the column is less than 12, then it is called a short column.

2: Long column:
- When the ratio of the effective length to the minor radius of gyration is greater than 45, it is known as a long column.
- The load-carrying capacity of the long column is less than the short columns.
- Its load-carrying capacity depends on the slenderness ratio (if the slenderness ratio of the column increases, then the load-carrying ability of the column decreases).
- When the length of the column is such that the buckling needs to be considered, and the queue is referred to as a slender column.
3: Intermediate column:
The column is intermediate when,
4d < L < 30d
Basic requirements for column design:
a) A minimum number of longitudinal bars in the compression member shall be 4 for bars within rectangular or circular ties, three for minimum and triangular relations, and 6 for bars within spirals.
b) The minimum number of longitudinal bars in the column is four within rectangular or circular ties.
c) The minimum number of longitudinal bars in the column is six numbers.
d) The precise distance between the longitudinal bars must not be less than 1.5 times the nominal bar diameter nor 1 ½ inch.
e) 40mm concrete cover should be provided then column to avoid the rusting of steel.
f) The center to center spacing of the ties or rings must not exceed the smaller 16 longitudinal bar diameter, 48 tie bar diameter.
Shear this article with your friends…..
We Love Cricket
thanks for sharing 🙂